Correlation
The relationship between two variables such that the change in one variable results in a positive or negative change in the other variable and also a greater change in one variable results in corresponding greater or smaller change in the other variable is known as correlation.
Coefficient of correlation
It is a measure of a tendency that is the degree to which two variables are interrelated is measured by coefficient which is called the coefficient of correlation. It is denoted by ‘r’.
Types of correlation
- Positive correlation
When direct relationship between two variables. Example height and weight of an individual
- Negative correlation
Inverse relationship between two variables. Example Price and Demand of a commodity.
- Linear correlation
When the plotted (x, y) are approximately on or near about a straight line. Example savings and earnings of a person.
- Perfect correlation
If the deviation in one variable is followed by a corresponding and proportional deviation then the correlation is said to be perfect correlation.
Pearson Correlation Coefficient Formula:
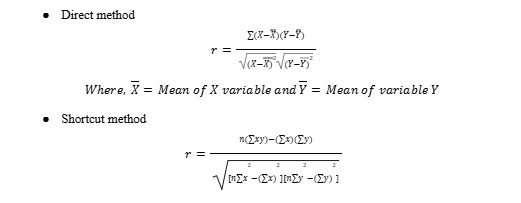
where, n = Quantity of Information
Σx = Total of the First Variable Value
Σy = Total of the Second Variable Value
Σxy = Sum of the Product of & Second Value

